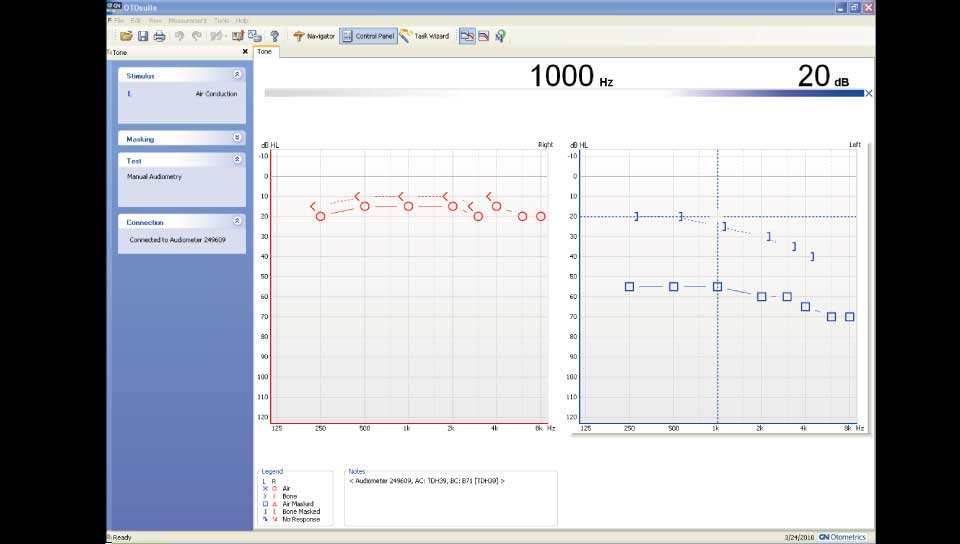
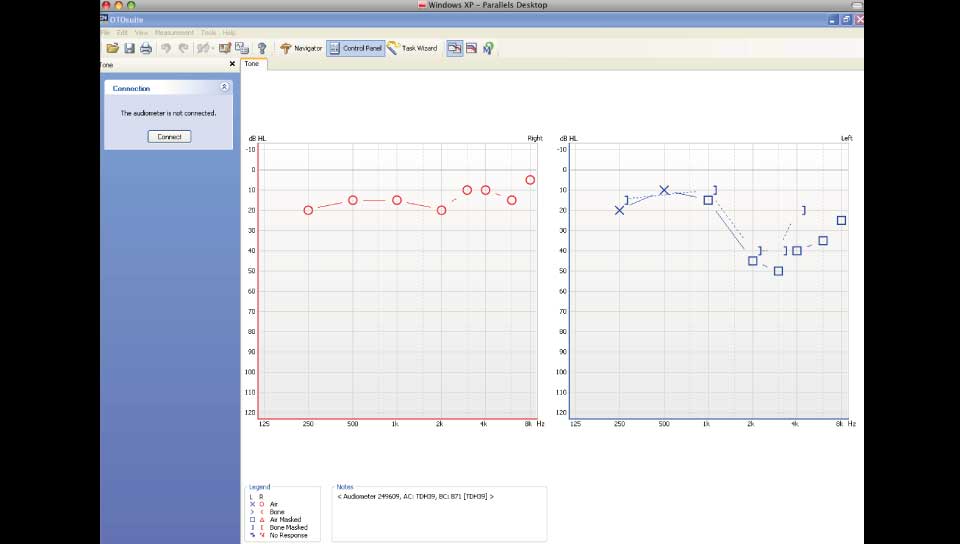
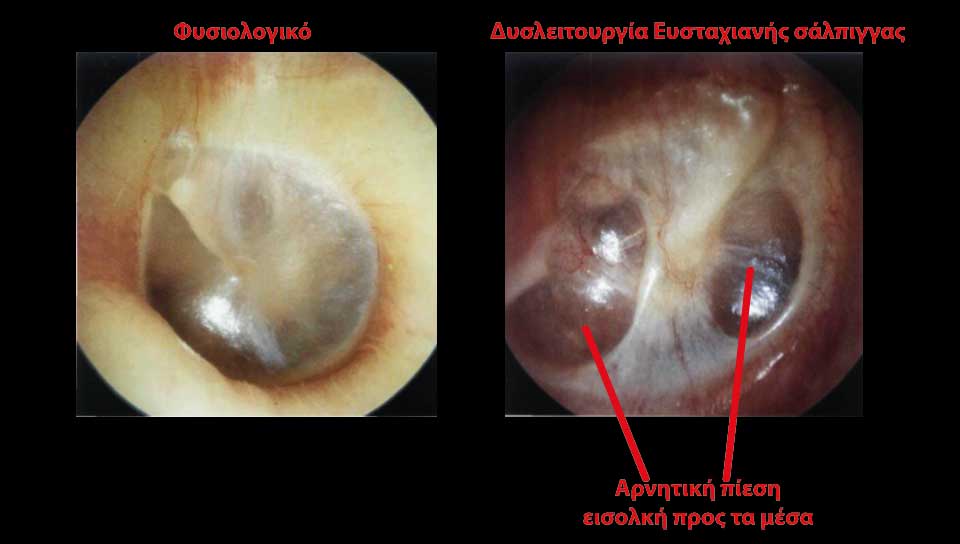
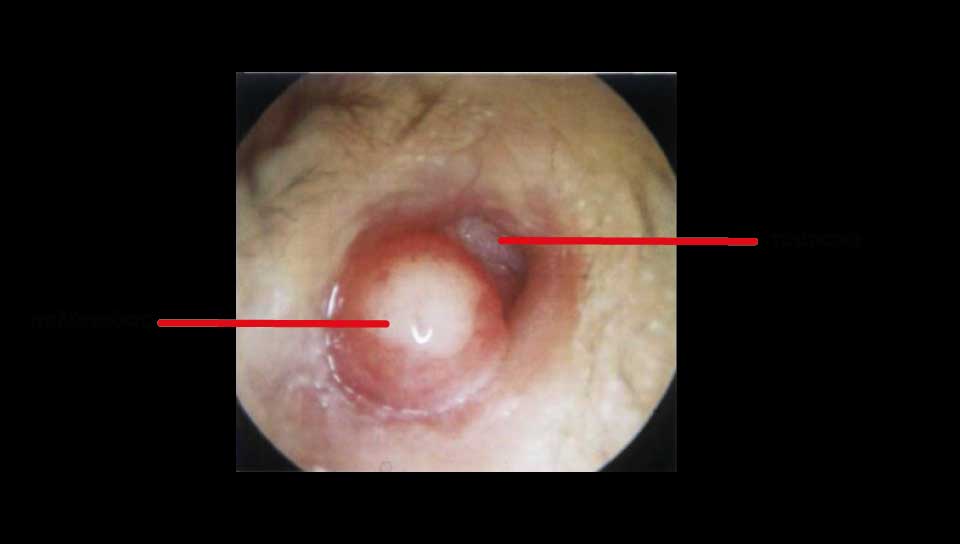
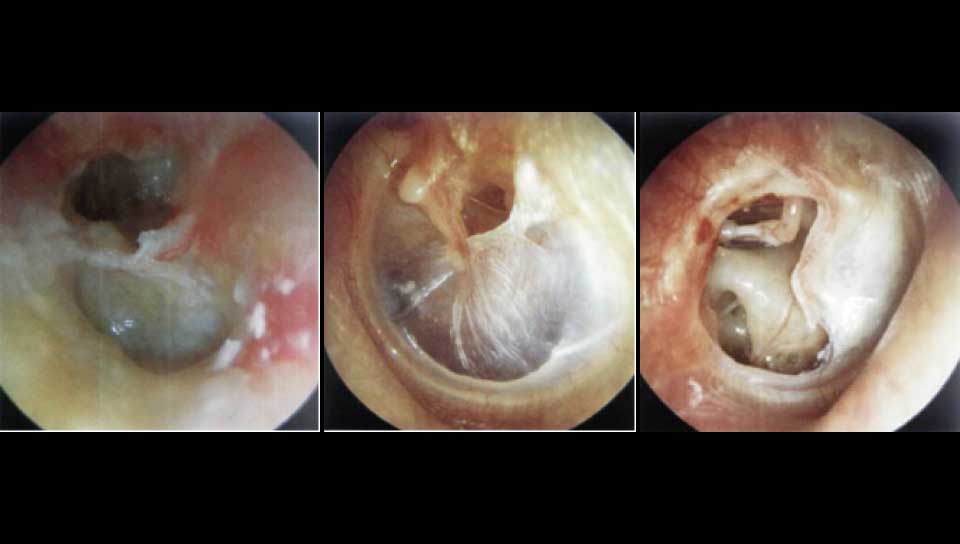
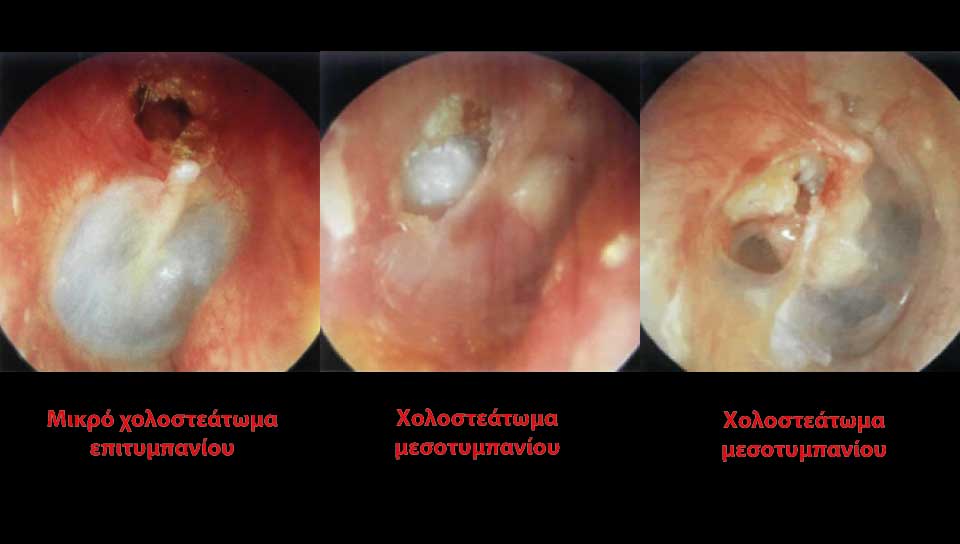
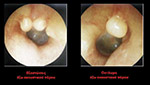
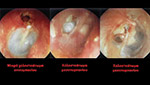
Eardrum perforations could be acute or chronical. Acute perforations usually appear after an injury or a severe inflammation and don't usually demande surgical restoration. Even very severe post-traumatic ruptures can be healed alone. Surgical restoration is usually related to chronic otitis media, which is a chronic inflammation of the mid-ear (behind ear-drum) because of which the perforations stay open. It also becomes the entrance for bacterias, that's why special care should be taken in order to prevent water or dirt from entering the ear, especially while bathing, washing one's hair etc. There is usually pus discharge from the ear and hearing reduction. In some cases an otitis is cholosteatomous, which means that, inside the middle ear area, a mass is being produced that damages the healthy tissues. In both of these otitis types there can be an expansion of the infection: 1. to the facial nerve (which is responsible for the movements and frowns of the face) leading to an alteration of the shape of the face. 2. to ear parts which are responsible for hearing and balance, so we may have a severe loss of hearing, tinnitus or/and vertigo and dizziness. 3. to the brain, with danger of meningitis, encephalitis, brain abcess etc, with very grave consequencies.
The operation
Depending on the type of the problem, we can choose to do several different types of tympanoplasty. Removal of the pathological tissue and perforation restoration with the use of transplant taken from the same area through the same incision. The incision is made in the back of the ear and is not visible.
Stages
- A little incision is made postauricular, where the ear meets the scull, so it is not visible after the surgery
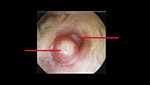
- We lift the eardrum.
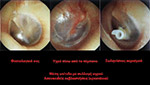
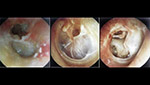
- We remove any pathological tissue from the mid ear (the area behind ear drum). We remove polyps, cholosteatoma etc
- We take transplants using the same incision. The transplants are parts of fascia or cartilages depending on the problem
- We place the transplant(s) where the rupture has been made covering it completely
- We bring the eardrum back to its normal position and then we make a slight packing of the external ear canal
Anesthesia
General
Duration of surgery
45 minutes to 3 hours
Stay in the clinic
2 days
Result
The results are permanent if causes of the situation like hypertrophic adenoids, severe deviated septums etc. are taken care of.
Combination with other operations
There cannot be another operation the same day. If a related problem appears there can be adenotomy, tonsillectomy or nasal septoplasty beforehand
Instructions after surgery
- Immediate mobilization after the surgery
- The ear remains with a slight packing for a week
- The removal of the packing is made by the surgeon
- Ear drops are being used for about a month after the packing removal
- No painkillers are needed
- Antibiotics are being given as a preventive measure and only for as long as the bandage remains




 Press here to download a free QR Reader
Press here to download a free QR Reader



