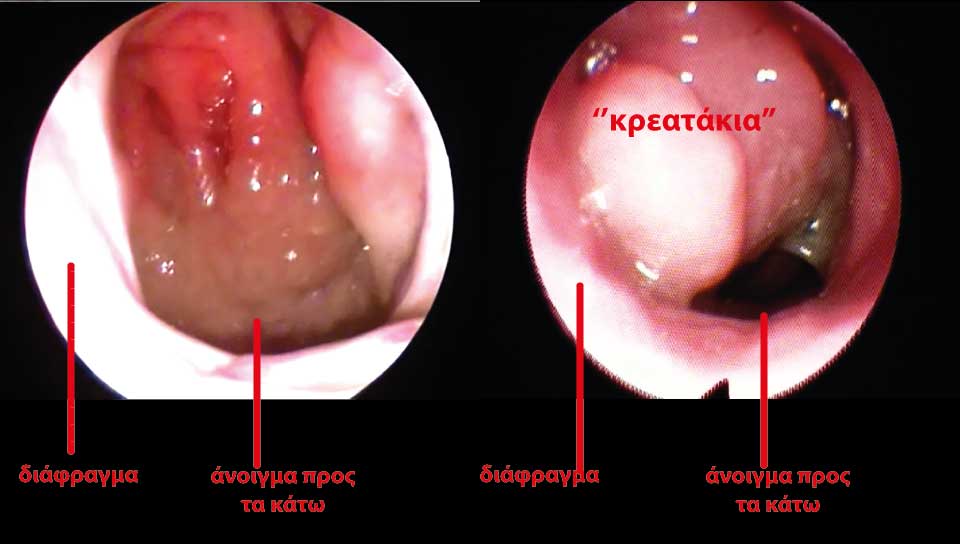
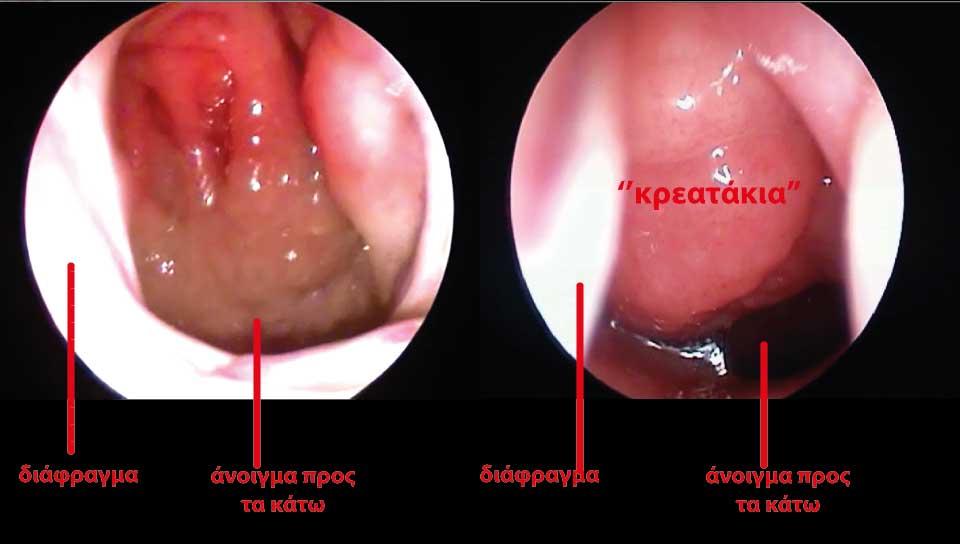
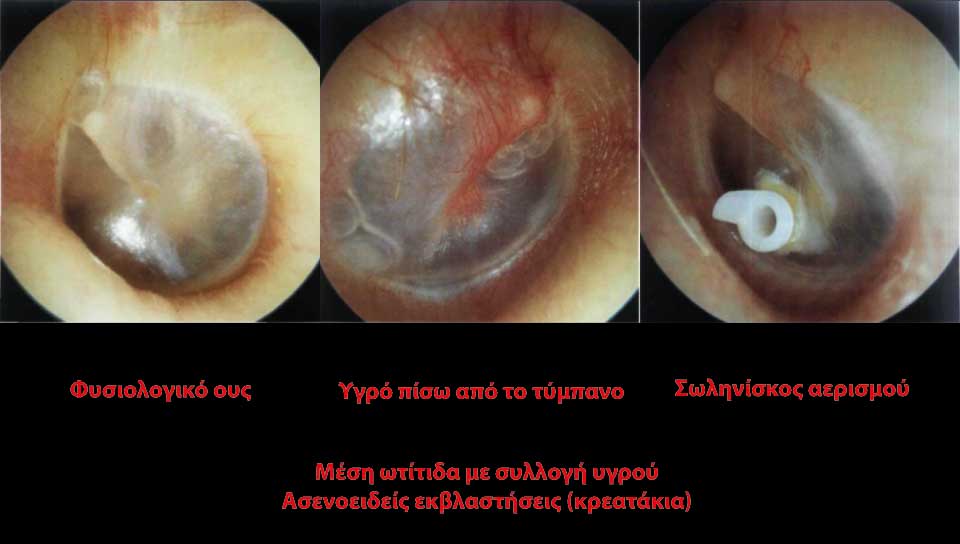
The Adenoids are found in the back of the nose and under normal circumstances don't cause any special problems. When their size gets bigger (hypertrophy), then there can appear: 1. Difficulty while breathing by nose because they can even block totally the entrance of the air 2. Eustachian tube disfunction (of even blocage), which leads to otitis media with effusion (OME). When a child cannot breath by the nose, it has to open the mouth many - many times during the day. Usually kids with Adenoidal hypertrophy have a delay in body development, suffer from lack of concentration in school, snore and they often look “tired”. Another fact should also be pointed out: Normally, kids have a palate that has the shape of a dome and as time goes by, its shape becomes more flat with the help of tongue that "pushes" upwards. When a child suffers from adenoidal hypertrophy, mouth remains open, the tongue cannot push the palate upwards, the up jawbone is not properly developped so we have a narrower upper jaw-bone and teeth problems (not enough space for the teeth) as well as a change in the shape of a child's face and head. As a result we have the so-called “adenoid face” with a very characteristic shape of “suppressed” face, which looks narrower and longer than normal The problem with the eustachian tube is the following: The eustachian tube (ET) is a little tube that starts from the back of the nose and is the valve that balances the pressure in the ear so it can function properly. When this valve (ET) is being pressed by the enlarged adenoids then it shuts down, the ear has no connection with the back of the nose, by extension with the environment, negative pressure is being produced (“sucked” inside), fluid is being gathered behind ear drum, which gets thicker and thicker (middle ear otitis with effusion) and finally we have a loss of hearing and permanent damages.
The operation
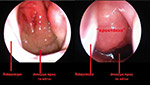
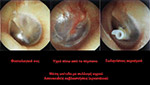
The operation is called adenotomy (adenoidectomy) and consists in the removal of the hypetrophic adenoids by the use of conventional equipment, ultrasound cutter, radio- frequencies or Laser
Stages
- Placing the kid inTrendelenburg Position (supine and head lower than the body) with open mouth and examination of the nose and the pharynx area with a mirror or an endoscope
- Removal of hypetrophic adenoids by the use of conventional equipment, ultrasound cutter, radio- frequencies or Laser
- Stop of the bleeding of the area
- No sutures are required
- Ear examination for Otitis media with effusion (fluid gathering behind eardrum) and in case of such gathering there may tympanic membrane incision (myringotomy - tympanotomy) and probably placement of ear tubes so the ear can be easily ventilated
- If there is tonsillectomy indications, extraction of the two tonsils with the use of conventional equipment, ultra-sound chisel, radio frequency or Laser
Anesthesia
General
Duration of surgery
20-30 minutes
Stay in the clinic
Discharge 6 hours after surgery. In combination with other operations as tonsils removal, discharge is given the day after.
Result
Permanent and immediate results.
Combination with other operations
Depending on the case, there can be combination of the following operations: Adenotomy, tonsillectomy, placement of ventilating tubes. In kids we don't perform a nasal septoplasty or lower nasal concha cauterisation except from really rare occasions (for example incapability of eating, growth delay etc)
Instructions after surgery
- Immediate mobilization after the surgery
- No suture removal because sutures are not being placed
- No painkillers required
- Antibiotics given as precaution only for 4 days
- If tonsils removal has been made or air-tubes have been placed then instruction should be followed as given in the related texts









 Press here to download a free QR Reader
Press here to download a free QR Reader



